JS Compression
In the bustling streets of the web, every byte counts. JS (JavaScript) Compression serves as a meticulous craftsman, shaving off the unnecessary parts of your JavaScript, ensuring it runs swiftly without wasting any resources.
What is JS Compression?
Imagine a librarian who efficiently organizes vast amounts of information into compact, easy-to-access sections. JS Compression acts similarly for JavaScript files. It optimizes scripts by removing unnecessary characters, spaces, and comments and sometimes even renaming variables to shorter names, resulting in a file that performs the same tasks in less space.
Why is JS Compression Essential?
In today's digital age, user experience hinges on speed and seamless interaction. The size of your website's files plays a pivotal role in this. Compressing your JavaScript files significantly reduces their weight, ensuring they consume less bandwidth and load at lightning speed. This translates to quicker interactions and a smoother, more responsive user experience. Here's why compressing your JavaScript is non-negotiable:
- Faster User Experience: Compressed JS files equate to quicker download times, meaning users can interact with your site's features without frustrating delays.
- Economical Bandwidth Usage: Smaller file sizes mean your website consumes less bandwidth, which can be particularly beneficial if you're dealing with a large volume of traffic.
- Optimized Server Performance: By combining multiple JavaScript files into a single compressed file, you reduce the number of HTTP requests. This lightens the load on your server, allowing it to serve more visitors efficiently.
- Unnecessary Elements Be Gone: JavaScript execution doesn't require comments and excessive whitespace. By eliminating them, you reduce file size and boost script execution times, ensuring your site functions swiftly and efficiently.
JS compression isn't just about conserving space; it's about enhancing every user's experience—making every interaction on your site feel instantaneous and fluid.
Understanding JS Compression in Action
Before Compression:

After Compression:
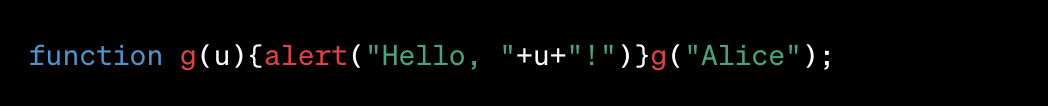
In this example, the function and variable names have been shortened, and unnecessary spaces and line breaks have been removed. The functionality remains unchanged, but the script is now more compact.
Implementing JS Compression: Steps to Sleek Scripts
- Backup Your Original Scripts: Always retain a copy of the uncompressed JS for future edits.
- Choose a JS Compressor Tool: Tools like UglifyJS or JSCompress can help you minify your scripts.
- Compress and Replace: Replace the original script on your site with the compressed version for faster load times.
- Test the Functionality: Ensure the compressed script works as intended without breaking any functionality.
Do's and Don'ts For JS Compression
✅ Do's:- Regularly Update: Compressed files should be updated when the original scripts change.
- Use Source Maps: They help debug the compressed code by mapping it back to the source.
- Combine Files: Where possible, merge multiple JS files into one before compression to reduce HTTP requests.
- Forget Backups: Always keep the original files. You'll need them for future edits.
- Compress Without Testing: Always test to ensure scripts run correctly after compression.
- Overlook Caching: Ensure compressed scripts are cached to improve load times further.
Conclusion
JS Compression is akin to a tailored suit; it fits better and enhances performance. By compressing JavaScript files, you're speeding up your website, enhancing user experience, and improving your search ranking.
FAQs
JS Compression reduces the size of JavaScript files by removing unnecessary characters and optimizing code, leading to faster page loads without sacrificing functionality.
Use tools like UglifyJS, Terser, or online platforms like JSCompress. Upload or input your script, and these tools provide a compressed version.
Properly compressed JS should not impact functionality. However, always test your site after implementing changes to ensure everything runs smoothly.
The uncompressed version is human-readable and essential for future edits, updates, or debugging. The compressed version is optimized for browsers, not for human understanding.
