Broken Link
A meta title, often called a "title tag," is essentially the title of a webpage. Think of when you search for something on Google. It's analogous to a book's title on a shelf, providing the initial allure and a snapshot of what lies within, beckoning you to open and delve deeper.
What is a Meta Title?
The meta title is an HTML element that denotes the title of a webpage. It appears prominently on search engine results pages (SERPs) and on the browser tab. A strategic meta title can significantly impact click-through rates from SERPs, making it essential for user engagement and SEO.
How to Implement the Meta Title
HTML encapsulates the meta title within a webpage's <head> section through the <title> tag. Here's a simple example:

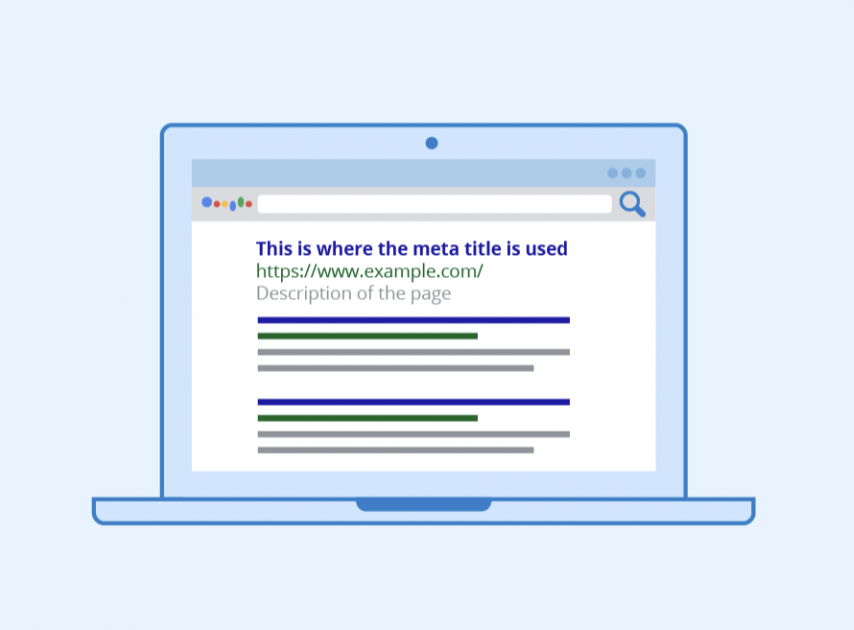
Examples of How Meta Titles Look
On the page’s HTML markup:

On the SERPs page:
Top browser tab of the page:

Why Does a Meta Title Matter?
- First Impressions Count: A compelling and relevant title can be the difference between someone clicking on your link or passing it by.
- It's the Search Engine's Compass: Search engines use the meta title to understand the page's content and rank it accordingly.
Do's and Don'ts of Meta Titles
✅ Do's- Keep it Crisp: Use 50–60 characters to avoid truncation in search results.
- Integrate Keywords Judiciously: Include exact match keywords naturally.
- Ensure Accuracy: Make sure the title truly reflects the page content.
- Avoid Keyword Overkill: Don’t spam keywords.
- Diversify Your Titles: Avoid using identical titles for multiple pages.
- Embrace Your Brand: If recognized, include your brand name in the title.
Good vs. Bad Meta Title Examples
Good Titles:- "Quick & Easy Vegan Chocolate Cake Recipe - Delightful Desserts"
- "Top 10 Running Shoes of 2023: Expert Reviews"
- "Ultimate Guide to Growing Roses in Temperate Climates"
- "Vegan Chocolate, Chocolate Vegan, Vegan Cakes, Cakes Vegan"
- "Homepage"
- "Page 1, Page 2, Page 3"
Are Title Tags an SEO Ranking Factor for Google?
Yes, they are! Google's John Mueller has emphasized the importance of title tags, stating, "Titles are important. They are important for SEO. They are used as a ranking factor." However, it’s one of many factors.
Conclusion
The meta title is more than just a label. It's a powerful tool that, when used effectively, can improve website visibility, engage users, and enhance branding. Proper optimization of the meta title is crucial for SEO success and providing a better user experience.
FAQs on Broken Links
Broken links are links that no longer work and lead to an error page such as 404 (Not Found), 410 (Gone), or other failed responses instead of the intended destination.
Broken links happen when a page is deleted, the URL changes, a domain expires, a redirect is removed, or the linked page is temporarily unavailable.
Broken links don’t automatically destroy rankings, but too many broken internal links can waste crawl budget, create poor user experience, and weaken internal linking signals—especially if important pages become hard to reach.
Yes. Broken outbound links can reduce trust and user experience because visitors can’t access the referenced sources. It’s best practice to regularly audit and fix them.
A 404 means the page was not found and may return later. A 410 means the page is intentionally gone and is less likely to return. Both can be “broken links” depending on context.
Update the link to the correct URL, restore the missing page, or create a 301 redirect from the old URL to the most relevant new page.
Not always. Redirect only when there is a relevant replacement page. If there’s no meaningful match, it’s often better to serve a 404/410 and remove the internal links pointing to it.
It depends on how often your site changes, but checking monthly is a good baseline. Large or frequently updated sites may benefit from weekly checks.
Not directly, but broken links can increase bounce rate and reduce engagement, which impacts overall user experience. They can also cause unnecessary navigation attempts and wasted requests.
A broken link checker crawls your pages, extracts URLs, and then tests each link to see if it returns a successful HTTP status code (like 200) or an error/timeout.
