JS Compression
JavaScript compression reduces the size of JavaScript files without changing how they work.
- JavaScript compression removes unnecessary characters like spaces, comments, and line breaks.
- Smaller JavaScript files load faster, improving website speed and performance.
- Faster loading JavaScript enhances user experience and can reduce bounce rates.
- Compressed JavaScript uses less bandwidth, which is especially helpful for mobile users.
- JavaScript compression is a best practice for performance optimization and technical SEO.
What is JavaScript Compression?
JavaScript compression is the technique of reducing the size of JavaScript files by removing unnecessary characters that are not required for execution. This typically includes extra whitespace, comments and line breaks which may be necessary for readability purpose.
The compressed version of a JavaScript file behaves exactly the same as the original code, but it is smaller in size, so it loads faster and consumes less bandwidth.
JavaScript compression is commonly used in production environments to improve website performance and ensure pages load quickly for users across different devices and network speeds.
Let's take a simple example to understand how JavaScript compression works.
Before Compression:

After Compression:
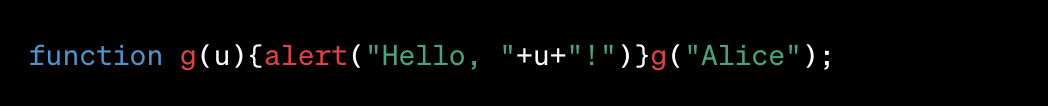
In this example, the function and variable names have been shortened, and unnecessary spaces and line breaks have been removed. The functionality remains unchanged, but the script is now more compact.
Why Does JavaScript Compression Matters?
JavaScript is a core technology used in modern websites to create interactive and dynamic user experiences. However, large or unoptimized JavaScript files can significantly slow down page loading speed and negatively impact user experience.
Here’s why JavaScript compression is important for websites:
- Improves page load speed: Smaller JavaScript files download faster, especially on slow mobile networks or unstable network connections.
- Enhances user experience: Faster JavaScript execution leads to smoother interactions and reduced user frustration.
- Supports better SEO performance: Page speed is an important ranking signal and compressed JavaScript files helps improve Core Web Vitals.
- Reduces bandwidth usage: Compressed files use less data and server bandwidth, benefiting both users and server resources.
- Optimizes mobile performance: Mobile users gain the most from reduced file sizes and quicker execution.
JavaScript compression is one of the simplest yet most effective optimizations you can apply to improve website speed, usability and overall technical performance.
JavaScript Compression vs JavaScript Minification
People often use the terms JavaScript compression and JavaScript minification interchangeably,thinking they both mean the same thing. The fact is that JavaScript compression and JavaScript minification are closely related. but they don’t always mean the exact same thing.
JavaScript minification is mainly about removing characters that don’t affect how the code runs. This includes:
- Extra spaces, tabs, and line breaks
- Comments meant only for developers for readability and understanding the purpose of a piece of code
- Indentation and formatting used for maintaining code and improving readability
JavaScript compression usually goes a step further by applying additional "size reduction techniques" such as:
- Shortening variable and function names (e.g. "totalPrice" becomes "p").
- Rewriting expressions into smaller equivalent statements which takes less space on disk.
- Removing unused and redundant code which is no longer necessary.
In simple terms - minification makes your code smaller by removing “visual” clutter, while compression can make it even smaller by restructuring parts of the code which can be more efficient. Many modern JavaScript compression and minification tools perform both type of operations, and the final output is still valid JavaScript that runs exactly the same as the original code.
For best results, keep your original source files for editing and debugging and serve the compressed or minified version to real users in production.
Do's and Don'ts of JavaScript Compression
Do's
- Compress JavaScript for production: Serve compressed and minified JavaScript files to visitors instead of serving development versions of JavaScript files.
- Keep the original source code as it is: Always store a readable version of your JavaScript for future edits and maintenance.
- Test after compression: Run a quick functionality check on your website to ensure your scripts still work as expected and there are no conflicts with other files.
- Use source maps when possible: Source maps help you debug issues by mapping compressed code back to the original files.
- Combine compression with caching: Compressed files load even faster when paired with JavaSCript caching and CSS caching.
- Automate the process: Integrate compression into your build or deployment workflow so it happens consistently without any human intervention.
Don’ts
- Don’t edit compressed files manually: They’re difficult to read and easy to break, always edit the original source files and compress them properly.
- Don’t assume compression fixes poor code: Compression reduces file size, but inefficient JavaScript can still slow down your website. Code optimisation should be a separate exercise altogether.
- Don’t forget debugging needs: Without source maps, troubleshooting compressed code becomes much harder. Use source maps for debugging purpose.
- Don’t compress already compressed files: Re-compressing already compressed files usually provides minimal benefits and can introduce errors or inconsistencies.
- Don’t ignore performance testing: Use tools like Lighthouse or PageSpeed Insights to confirm that compression improves page speed performance.
- Don’t rely on only one optimisation technique: Compression works best when combined with other optimizations like code splitting and removing unused scripts.
Is JavaScript Compression Good for SEO?
Even though JavaScript compression is not a direct ranking factor but it indirectly influences page load speed, performance, and user experience which has a co-relation with SEO and Rankings.
Search engines focus on delivering fast, reliable, and user friendly results. Website performance is a critical part of this, and JavaScript compression helps improve performance by reducing file size and page load time.
Compressed JavaScript files download faster and execute more efficiently in the browser, which contributes to quicker page rendering. Faster pages provide a better user experience, leading to stronger engagement signals such as lower bounce rates and longer time on site.
JavaScript compression also supports better Core Web Vitals performance. By minimizing the amount of JavaScript that needs to be processed, it can positively influence metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
From a crawling and indexing perspective, lightweight JavaScript reduces server and network overhead, making it easier for search engines to access and process your webpages. Especially if your website is large or using a lot of JavaScript heavy files, compression really helps search engines render your pages faster which improves crawling and indexing of your content in search engine's database.
While compression alone won’t push a page to the top of search results, it strengthens the technical foundation of your site. When combined with clean code, proper rendering, and high quality content, JavaScript compression becomes an important part of a solid SEO and performance optimization strategy.
Best JavaScript Compression & Minification Tools
- JSCompress - An online JavaScript compressor that lets you paste or upload JavaScript files and compress them up to 80% of the original file size. It uses reliable minification engines and keeps functionality intact.
- Toptal JavaScript Minifier - An online minifier and compressor from Toptal that quickly reduces JavaScript file size. It also supports API access for workflow automation.
- Minify-JS.com - A browser-based tool powered by Terser that handles modern JavaScript (ES6+) and offers configuration options for more advanced control.
- JavaScript Minifier (OnlineTools) – A browser tool that strips whitespace, comments, and redundant code quickly and securely, without uploading your files.
- UglifyJS - A long standing Node.js based minification library that parses, minifies, and compresses JavaScript, with optional source map generation. It’s great for build processes and CLI workflows.
- esbuild - A modern, high speed bundler and minifier written in the programming language "Go". It supports ES6+ syntax and can process very large codebases extremely fast, making it ideal for production builds.
- Google Closure Compiler - More than just a JavaScript minifier, this advanced tool analyzes and rewrites JavaScript for maximum optimization and dead code removals, suitable for large or complex applications.
- JSMin - A simple and minimalist command line tool which helps remove whitespace and comments to shrink code size reliably.
FAQs
JS Compression reduces the size of JavaScript files by removing unnecessary characters and optimizing code, leading to faster page loads without sacrificing functionality.
Use tools like UglifyJS, Terser, or online platforms like JSCompress. Upload or input your script, and these tools provide a compressed version.
No. Compression reduces file size at the code level, while Gzip compresses files during transfer. Both should be used together.
Yes, although external JavaScript files benefit more from compression.
While it is possible to reverse compressed JavaScript to uncompressed JavaScript, compressed code is difficult to read and not intended for editing. In Some situations, the reversals may not be accurate, depending upon the compressor differences which were used to compress and de-compress a file.
Properly compressed JS should not impact functionality. However, always test your site after implementing changes to ensure everything runs smoothly.
The uncompressed version is human-readable and essential for future edits, updates, or debugging. The compressed version is optimized for browsers, not for human understanding.
